Good oral hygiene protects more than just your teeth—it also improves heart health. Bacteria from gum disease enter the bloodstream, increasing inflammation and heart disease risk. Poor oral health raises the chances of high blood pressure, stroke, and heart attacks. Brushing, flossing, and regular dental checkups reduce plaque and gum inflammation. Healthy gums improve blood flow and lower heart strain. Treating gum disease reduces systemic inflammation and improves overall cardiovascular function. Understanding the link between oral and heart health helps prevent serious complications. Let’s explore how maintaining good oral hygiene strengthens both your smile and your heart.
The Link Between Oral Health and Heart Health
Gum disease increases the risk of heart disease by raising inflammation levels. When plaque builds up along the gumline, bacteria enter the bloodstream through inflamed gum tissue. These bacteria trigger an immune response, increasing blood vessel inflammation and narrowing arteries. Narrowed arteries reduce blood flow, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. Periodontitis also increases C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, which indicate inflammation and heart strain. Treating gum disease lowers CRP levels and reduces heart disease risk. Improved gum health strengthens blood vessels and reduces blood pressure. Better oral hygiene supports healthier circulation and stronger heart function.
How Gum Disease Affects the Cardiovascular System
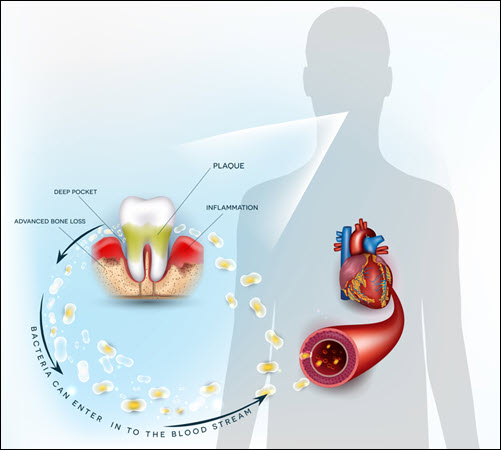
Gum disease allows harmful bacteria to enter the bloodstream. Once in the blood, these bacteria stick to the walls of blood vessels. This creates plaque buildup in the arteries (atherosclerosis), which restricts blood flow and increases heart strain. Inflammation from gum disease increases clotting risk, which leads to heart attacks and strokes. High levels of oral bacteria also weaken the heart’s lining, increasing the risk of endocarditis (heart infection). Chronic gum inflammation raises blood pressure and reduces oxygen flow to the heart. Treating gum disease improves blood vessel health and reduces heart attack and stroke risk. Healthier gums strengthen heart function and overall circulation.
How to Improve Oral Health and Protect Your Heart
Brushing and flossing daily prevent plaque buildup and gum inflammation. Brush twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles between teeth. Use an antibacterial mouthwash to kill harmful bacteria and freshen breath. Regular dental cleanings remove tartar and improve gum health. Eating a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins strengthens gum tissue and reduces inflammation. Drinking water increases saliva production, which protects teeth from plaque. Avoid smoking and alcohol, which increase gum inflammation and heart strain. Proper oral hygiene improves gum strength and reduces heart disease risk.
Benefits of Treating Gum Disease for Heart Health
Treating gum disease lowers inflammation and improves blood flow. Scaling and root planing remove plaque and tartar beneath the gumline. This reduces gum inflammation and improves gum attachment to teeth. Antibiotic treatments reduce harmful bacteria and improve healing. Better gum health lowers CRP levels and reduces heart strain. Improved blood vessel function decreases the risk of high blood pressure and stroke. Strengthened gum attachment increases tooth stability and reduces sensitivity. Better gum health reduces the spread of harmful bacteria to the heart. Treating gum disease supports healthier circulation and improves overall heart function. Stronger gums increase both dental and cardiovascular health.
Signs of Poor Oral Health Affecting Heart Health
Red, swollen, and bleeding gums signal early gum disease (gingivitis). Persistent bad breath results from plaque buildup and bacterial growth. Loose teeth and gum recession reflect weakened gum attachment and inflammation. Tooth sensitivity to hot and cold signals enamel erosion and gum exposure. Increased plaque and tartar buildup increase cavity risk and gum irritation. Gum infections increase overall inflammation and affect blood pressure. Heart palpitations and shortness of breath reflect poor circulation caused by narrowed arteries. Regular dental checkups detect early signs of gum disease and heart-related complications. Treating oral health issues strengthens gum and heart function.
Long-Term Protection for Oral and Heart Health
Regular dental checkups prevent plaque buildup and improve gum health. Dentists recommend professional cleanings every six months to maintain healthy gums and teeth. Brushing and flossing daily prevent gum inflammation and bacterial growth. Managing stress reduces jaw clenching and gum sensitivity. Eating a nutrient-rich diet strengthens gum tissue and improves immune response. Staying hydrated improves saliva production and protects enamel from plaque. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake improve both gum and heart health. Treating gum disease reduces inflammation and improves overall circulation. Proper care supports long-term heart health and stronger gums. Healthy gums protect teeth and improve cardiovascular function.
Good oral hygiene reduces inflammation and strengthens heart health. Brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash prevent plaque buildup and improve gum strength. Treating gum disease lowers blood pressure and reduces stroke and heart attack risk. Early detection of gum problems improves circulation and protects blood vessels. Professional dental cleanings and regular checkups strengthen gum health and improve heart function. A balanced diet and proper hydration reduce plaque and inflammation. Protecting gum health strengthens both teeth and heart function. Investing in oral care reduces heart disease risk and improves overall well-being. Stronger gums and a healthier heart create a confident, vibrant life.